

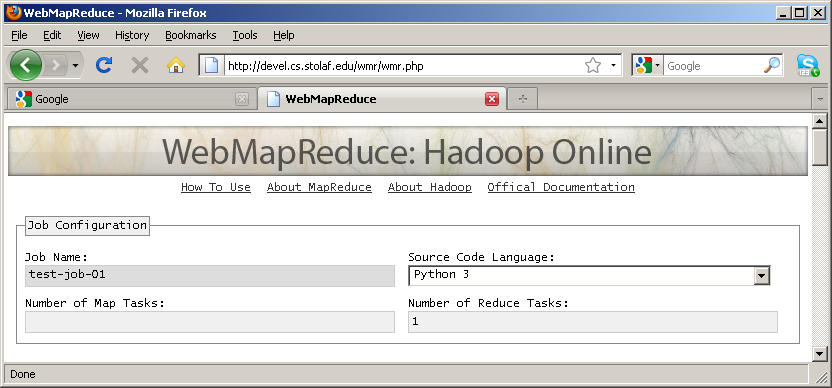
1 as the value:
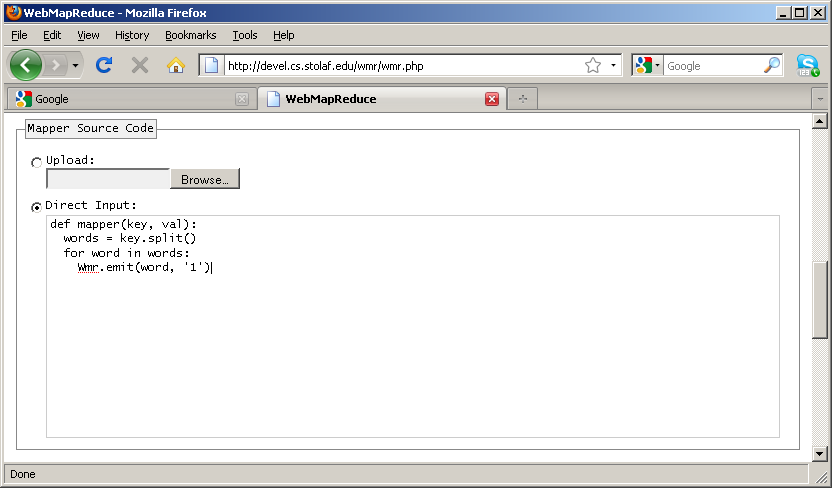
def mapper(key, val): words = key.split() for word in words: Wmr.emit(word, '1')
mapper(). This name is required so that WebMapReduce knows what function to call to feed input.[3] You are free to write other auxillary functions to support your mapper.
key and value. This is the input key-value pair described in the introduction to map-reduce. Both arguments will be strings.
Wmr.emit() function is how key-value pairs are output in the Python library for WebMapReduce. It takes two arguments: again, a key and a value.[5]
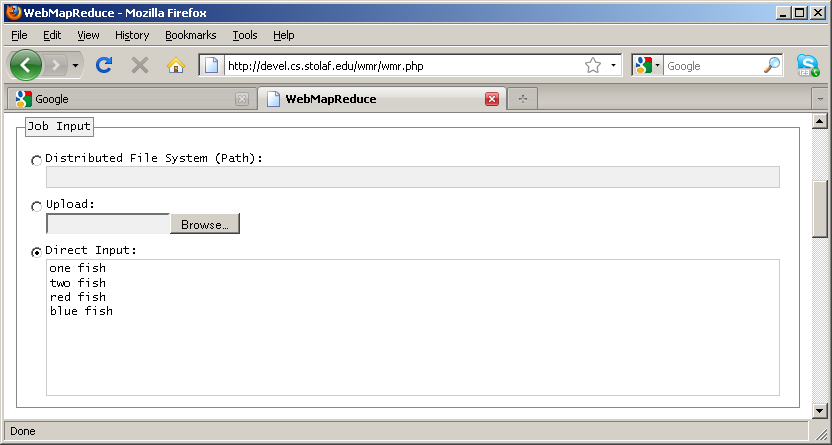
one 1 fish 1
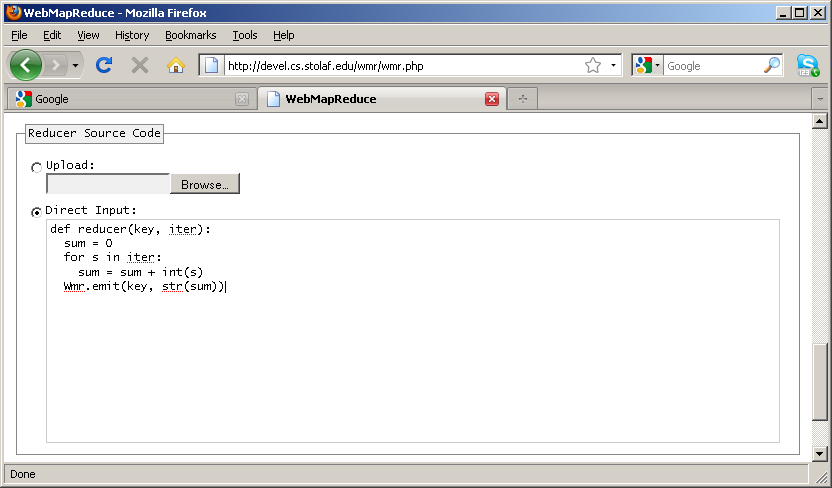
1's associated with each word to get a final count:
def reducer(key, values): sum = 0 for v in values: sum = sum + int(v) Wmr.emit(key, str(sum))
reducer(). As with mapper(), this is required.
reducer() is actually a list of values. This is the list of all values output from the map phase whose key was equal to key. As described in the introduction to map-reduce, the framework collects these values and generates the list automatically.
values is a list of "1"s with as many elements as there were occurrences of key in the input.
sum, each value is converted from a string to an integer using Python's int() function.
Wmr.emit(), the sum is converted from an integer to a string using Python's str() function. As with the mapper, this is not required, but is included to make the conversion explicit.
[3] All languages require certain names for mappers and reducers, although the exact name may differ. The chapter on each language will give the specific requirement.
[4] Although this is generally true in WebMapReduce, some languages may behave differently. These differences will be noted in the chapter for each language.
[5] Other languages may have similar functions, or they may use the return value of the function as output. See the chapter on each language.